For professionals in Life Sciences, ensuring data integrity throughout all stages of the Data LifeCycle is crucial. This article outlines the five key stages of Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) and the essential actions needed at each stage. DLM is fundamentally a policy-driven approach to managing the flow of data in an information system from its inception until its eventual obsolescence and deletion.
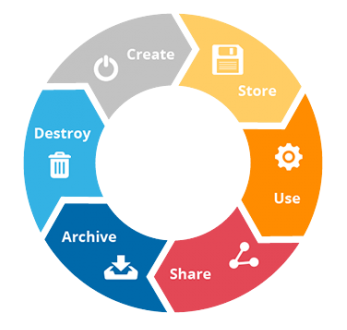
The Five Phases of Data Lifecycle Management
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) organizes the progression of data from creation to eventual destruction. Each phase of the data lifecycle, while interpreted differently across contexts, includes essential processes summarized below:
1. Data Creation
Creation or capture of data marks the beginning of its lifecycle. This data could be in various forms like PDFs, images, Word documents, or entries in a SQL database. Data generation happens through:
- Data Acquisition: This involves acquiring data that was created outside of the organization.
- Data Entry: Manually inputting new data by internal personnel.
- Data Capture: Using devices to collect data that is automatically generated during organizational processes.
Technological solutions for DLM help in automating the management and migration of data across different storage tiers according to pre-defined policies.
2. Storage
Post-creation, data must be securely stored and maintained with robust security measures, including a comprehensive backup and recovery system to protect data throughout its lifecycle. Proper storage ensures data remains intact, secure, and accessible, with additional processing like encryption and cleansing being part of this phase.
3. Usage
During this stage, data supports organizational functions by being accessed, processed, and modified. It is crucial to maintain an audit trail for critical data to track any changes made. Data sharing and collaboration within and outside the organization are facilitated during this phase, enhancing functionalities like analytics and visualization.
4. Archival
Archival is the process of storing data in a dormant state away from active environments, ensuring it remains accessible for future needs without the regular maintenance or active usage, adhering to compliance and analysis needs.
5. Destruction
As data accumulates and storage costs rise, it becomes necessary to purge unnecessary data securely, following all regulatory and compliance requirements, to maintain data hygiene and cost efficiency.
Effective Data Lifecycle Management Practices
A well-documented DLM process is essential for robust Data Governance, ensuring data security, privacy, and uninterrupted access. Data integrity, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data, is a key focus, along with ensuring data availability for authorized use without disrupting existing workflows.
At Dataworks, our team of expert CSV & Software Engineers provides top-tier Data Integrity services including assessments, remediation, and validation services. Our strategies incorporate a mix of procedures, best practices, and technological applications to optimize DLM, making data management more efficient and compliant.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Creation | Acquisition, entry, or capture of data in various forms. |
| Storage | Protecting and securing data with backup and recovery processes. |
| Usage | Viewing, processing, modifying, and saving data with audit trails. |
| Archival | Copying data to a storage environment for future use if needed. |
| Destruction | Removing all copies of unnecessary data after the retention period. |