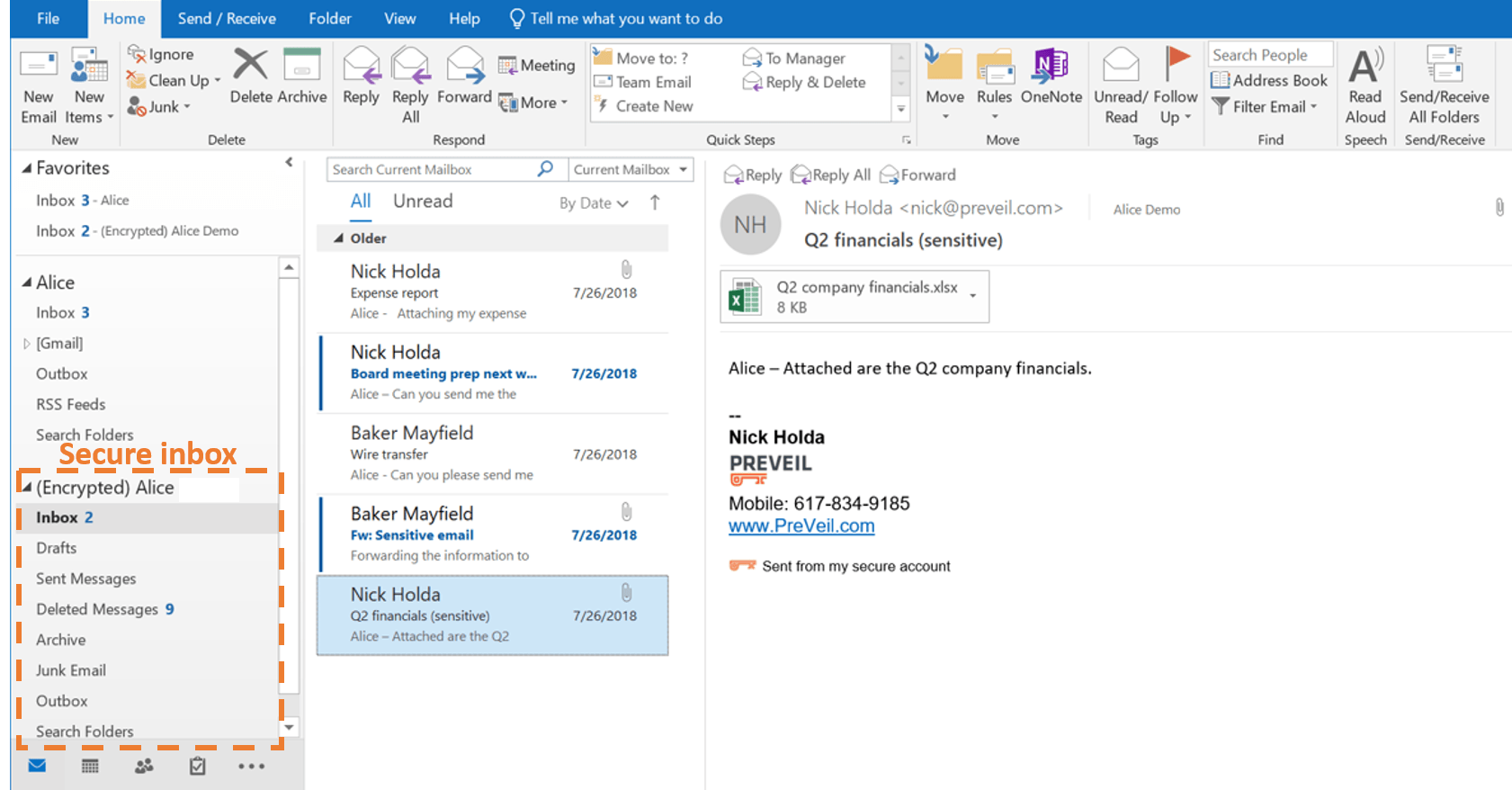
In the vast landscape of digital communication, securing sensitive information remains paramount, especially when sending emails through platforms like Outlook. Encryption, the art of transforming readable text into indecipherable cipher text, stands as a fortress safeguarding privacy. This guide delves into the practical steps to encrypt your emails in Outlook, ensuring they remain visible only to your intended recipients.
Understanding Email Encryption in Outlook
Encrypting an email in Outlook means converting it from plain text into scrambled cipher text. Only the recipient, holding the private key that matches the public key used to encrypt the message, can decipher it for reading. This process prevents unauthorized access, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential between the sender and the intended recipients. Outlook offers two encryption standards: S/MIME and Microsoft 365 Message Encryption, each catering to different user needs and setups.
Encrypting with S/MIME
The Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) standard enhances email security by allowing senders to encrypt emails using public keys. This method ensures that only recipients with the corresponding private keys can decrypt and read the messages. To use S/MIME in Outlook, one must first install a digital certificate to their device and then configure it within Outlook’s settings.
Encrypt with Microsoft 365 Message Encryption
For those subscribed to Microsoft 365, utilizing Microsoft 365 Message Encryption offers a streamlined approach to safeguarding emails. This feature, available through the Office 365 Enterprise E3 license, integrates seamlessly within Outlook, allowing users to encrypt messages directly through the email composition window. By selecting the “Encrypt” option, senders can impose restrictions such as “Encrypt-Only” or “Do Not Forward,” further enhancing the security of their communications.
Practical Steps for Encryption
- S/MIME Encryption: Begin by obtaining a digital certificate and adding it to your device. Within Outlook, navigate through the File menu to Options > Trust Center > Trust Center Settings. Here, select Email Security, then under Encrypted email, choose Settings and select your S/MIME certificate.
- Microsoft 365 Message Encryption: Simply start composing your email, then select the “Encrypt” button. Choose the appropriate encryption level, either “Encrypt-Only” or a more specific restriction like “Do Not Forward.”
Table: Outlook Encryption Options
| Encryption Type | Required Setup | User Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| S/MIME Encryption | Digital certificate on sender’s device | Enhanced security with public and private keys |
| Microsoft 365 Message Encryption | Microsoft 365 subscription | Easy-to-use encryption directly within Outlook with policy enforcement |
Why Encrypt?
Email encryption is not just about maintaining privacy; it’s a comprehensive approach to security, compliance, and even cost efficiency. In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats lurk at every corner, encrypting emails ensures that only the intended recipients can access the message contents. For businesses, this practice is not just beneficial; it’s often required to comply with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and more.
Final Thoughts: Securing Digital Dialogue
In the era of incessant cyber threats, encrypting your emails in Outlook is a proactive step toward securing digital communication. Whether for personal privacy or compliance with corporate policies, the encryption tools provided by Outlook offer robust solutions for protecting sensitive information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Outlook encryption available for all users?
- S/MIME encryption requires a digital certificate, while Microsoft 365 Message Encryption is available to subscribers of certain Microsoft 365 plans.
Can I encrypt emails for recipients outside my organization?
- Yes, both encryption methods allow for secure communication with external recipients, given the necessary setups are in place.
How do recipients decrypt my encrypted email?
- Recipients need the corresponding private key for S/MIME encrypted emails or must follow specific instructions for emails encrypted with Microsoft 365 Message Encryption.
Does encrypting an email change how I compose it?
- No, the composition process remains the same. Encryption is applied when sending the email.
Can encrypted emails be forwarded?
- Policies set during the encryption process, like “Do Not Forward,” can restrict forwarding.
Are attachments encrypted as well?
- Yes, when you encrypt an email, all contents, including attachments, are encrypted.
How do I know if an email I received is encrypted?
- Encrypted emails are usually indicated by a lock icon or similar symbol, depending on the email client used.